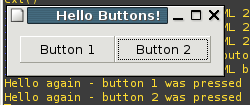
// gcc b0.c -o b0 `pkg-config --cflags --libs gtk+-2.0`
#include <gtk/gtk.h>
/* Our new improved callback. The data passed to this function
* is printed to stdout. */
static void callback( GtkWidget *widget, gpointer data)
{
g_print ("Hello again - %s was pressed\n", (gchar *) data);
}
/* another callback */
static gboolean delete_event(GtkWidget *widget,GdkEvent *event, gpointer data)
{
gtk_main_quit ();
return FALSE;
}
int main( int argc, char *argv[] )
{
/* GtkWidget is the storage type for widgets */
GtkWidget *window;
GtkWidget *button;
GtkWidget *box1;
/* This is called in all GTK applications. Arguments are parsed
* from the command line and are returned to the application. */
gtk_init (&argc, &argv);
/* Create a new window */
window = gtk_window_new (GTK_WINDOW_TOPLEVEL);
/* This is a new call, which just sets the title of our
* new window to "Hello Buttons!" */
gtk_window_set_title (GTK_WINDOW (window), "Hello Buttons!");
/* Here we just set a handler for delete_event that immediately exits GTK. */
g_signal_connect (G_OBJECT (window), "delete_event",
G_CALLBACK (delete_event), NULL);
/* Sets the border width of the window. */
gtk_container_set_border_width (GTK_CONTAINER (window), 10);
/* We create a box to pack widgets into. This is described in detail
* in the "packing" section. The box is not really visible, it
* is just used as a tool to arrange widgets. */
box1 = gtk_hbox_new (FALSE, 0);
/* Put the box into the main window. */
gtk_container_add (GTK_CONTAINER (window), box1);
/* Creates a new button with the label "Button 1". */
button = gtk_button_new_with_label ("Button 1");
/* Now when the button is clicked, we call the "callback" function
* with a pointer to "button 1" as its argument */
g_signal_connect (G_OBJECT (button), "clicked",
G_CALLBACK (callback), (gpointer) "button 1");
/* Instead of gtk_container_add, we pack this button into the invisible
* box, which has been packed into the window. */
gtk_box_pack_start (GTK_BOX(box1), button, TRUE, TRUE, 0);
/* Always remember this step, this tells GTK that our preparation for
* this button is complete, and it can now be displayed. */
gtk_widget_show (button);
/* Do these same steps again to create a second button */
button = gtk_button_new_with_label ("Button 2");
/* Call the same callback function with a different argument,
* passing a pointer to "button 2" instead. */
g_signal_connect (G_OBJECT (button), "clicked",
G_CALLBACK (callback), (gpointer) "button 2");
gtk_box_pack_start(GTK_BOX (box1), button, TRUE, TRUE, 0);
/* The order in which we show the buttons is not really important, but I
* recommend showing the window last, so it all pops up at once. */
gtk_widget_show (button);
gtk_widget_show (box1);
gtk_widget_show (window);
/* Rest in gtk_main and wait for the fun to begin! */
gtk_main ();
return 0;
}